EU's Strategy To Eliminate Russian Gas: Focus On The Spot Market

Table of Contents
Understanding the EU's Dependence on Russian Gas and the Need for Diversification
For decades, the EU heavily relied on Russia for its natural gas imports. This dependence created a significant vulnerability in the EU's energy security, making it susceptible to geopolitical pressures and supply disruptions. The war in Ukraine dramatically highlighted this vulnerability, forcing the EU to urgently seek alternative energy sources and diversify its gas supply portfolio. The need to reduce reliance on a single supplier, Russia, became paramount for ensuring energy independence and stability.
- Pre-war reliance percentages on Russian gas for key EU nations: Before the conflict, countries like Germany and Italy depended on Russia for a substantial portion (over 40%) of their natural gas needs. Other nations also had significant reliance, creating a collective vulnerability across the EU.
- Geopolitical risks associated with reliance on a single supplier: Dependence on a single supplier like Russia exposes the EU to political manipulation, price hikes, and potential supply cutoffs, as witnessed during the recent geopolitical crisis.
- EU's energy security goals and targets for reducing Russian gas imports: The EU has set ambitious targets to significantly reduce its dependence on Russian gas, aiming for complete independence in the coming years. This necessitates a rapid shift towards diverse sourcing and the development of alternative energy solutions.
The Role of the Spot Market in Securing Alternative Gas Supplies
The spot market for natural gas offers a flexible and dynamic platform for procuring gas from various sources. Unlike long-term contracts, the spot market allows for immediate purchases based on current supply and demand. This flexibility is crucial for the EU in its efforts to swiftly replace Russian gas. The EU is utilizing this market to source Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) from a wider range of countries, reducing reliance on pipelines originating from Russia.
- Advantages of spot market purchasing (flexibility, diverse sourcing): The spot market allows the EU to quickly adapt to changing geopolitical situations and explore new suppliers, increasing the resilience of its energy system.
- Disadvantages of spot market purchasing (price volatility, potential for supply shortages): The spot market is known for its price volatility, which can significantly impact energy costs for consumers and businesses. It also carries risks of potential supply shortages if global demand outpaces supply.
- Examples of countries the EU is sourcing LNG from (e.g., USA, Qatar, Norway): The EU is actively diversifying its LNG imports, securing supplies from North America (USA), the Middle East (Qatar), and Norway, among others.
- The role of LNG terminals in facilitating spot market transactions: The expansion of LNG import terminals across the EU is vital for receiving and processing LNG from diverse sources, making the spot market more effective.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies in Utilizing the Spot Market
The EU's reliance on the spot market for natural gas presents challenges. Price volatility, caused by global supply and demand fluctuations, poses a significant risk to energy security and economic stability. Potential supply disruptions, due to unforeseen global events or competition from other buyers, add further complexity.
- Impact of global gas price fluctuations on EU energy markets: The spot market's inherent price volatility can lead to sharp increases in energy costs for businesses and households, impacting economic growth and social well-being.
- Strategies for managing price volatility (hedging, long-term contracts): To mitigate price fluctuations, the EU can employ hedging strategies and consider a mix of spot market purchases and longer-term contracts for a degree of price stability.
- Importance of building strategic gas reserves: Strategic gas reserves provide a buffer against supply disruptions and price spikes, ensuring energy security during times of crisis.
- Investing in renewable energy sources as a long-term solution: The long-term solution to energy independence lies in a significant shift towards renewable energy sources, reducing the dependence on volatile fossil fuel markets.
The Importance of Infrastructure Development
Expanding the EU's energy infrastructure is paramount to effectively utilizing the spot market. This involves increasing the capacity of LNG import terminals to receive and process LNG from diverse sources and enhancing the pipeline network for efficient distribution of gas across the EU.
- Current LNG terminal capacity in EU countries: The EU is currently undertaking significant investments to expand its LNG import capacity, improving its ability to source gas from a wider range of suppliers.
- Planned expansion projects and their impact on import capacity: Numerous projects are underway to significantly increase LNG terminal capacity, enabling the EU to absorb larger quantities of LNG from the spot market.
- Interconnector projects to improve gas distribution within the EU: Improved interconnectors between EU countries ensure efficient distribution of gas from import terminals to consumers throughout the region.
The Future of the EU's Gas Supply and the Long-Term Strategy Beyond the Spot Market
The EU's long-term strategy extends beyond spot market reliance. It necessitates a fundamental shift towards energy independence by significantly increasing the share of renewable energy and improving energy efficiency.
- EU's renewable energy targets: The EU has established ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment, aiming to drastically reduce its dependence on fossil fuels.
- Investment in green technologies and energy efficiency programs: Investments in renewable energy technologies like solar, wind, and hydropower, coupled with energy efficiency improvements, are critical to the long-term energy transition.
- The role of hydrogen as a future energy source: Hydrogen, produced from renewable sources, is seen as a potential long-term solution for energy storage and transportation.
Conclusion
The EU's strategy to eliminate Russian gas relies heavily on its ability to effectively utilize the spot market for natural gas. While this approach offers flexibility and diverse sourcing options, it also presents challenges related to price volatility and supply security. Addressing these challenges through strategic reserves, infrastructure development, and a long-term commitment to renewable energy sources is crucial for achieving lasting energy independence. The successful implementation of this multi-pronged strategy will be essential for securing the EU's energy future and reducing its reliance on the volatile spot market for natural gas in the long term. Learn more about the intricacies of the EU's gas supply strategy and how the spot market plays a vital role in its transition to energy independence.

Featured Posts
-
 Bench Mob Hield And Payton Deliver For Warriors Against Blazers
Apr 24, 2025
Bench Mob Hield And Payton Deliver For Warriors Against Blazers
Apr 24, 2025 -
 California Gas Prices Governor Newsom Seeks Oil Industry Partnership To Lower Costs
Apr 24, 2025
California Gas Prices Governor Newsom Seeks Oil Industry Partnership To Lower Costs
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Real Estate Activity 65 Hudsons Bay Leases In High Demand
Apr 24, 2025
Real Estate Activity 65 Hudsons Bay Leases In High Demand
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Canadas Economic Vision Prioritizing Fiscal Responsibility
Apr 24, 2025
Canadas Economic Vision Prioritizing Fiscal Responsibility
Apr 24, 2025 -
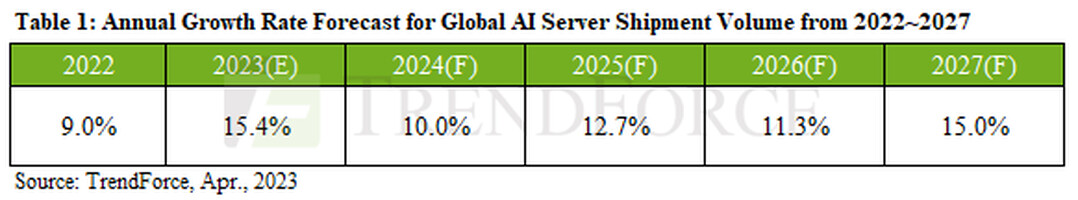 Sk Hynixs Dram Market Leadership Fueled By Ai Demand
Apr 24, 2025
Sk Hynixs Dram Market Leadership Fueled By Ai Demand
Apr 24, 2025
