Spot Market Crackdown: EU's Plan To End Russian Gas Imports
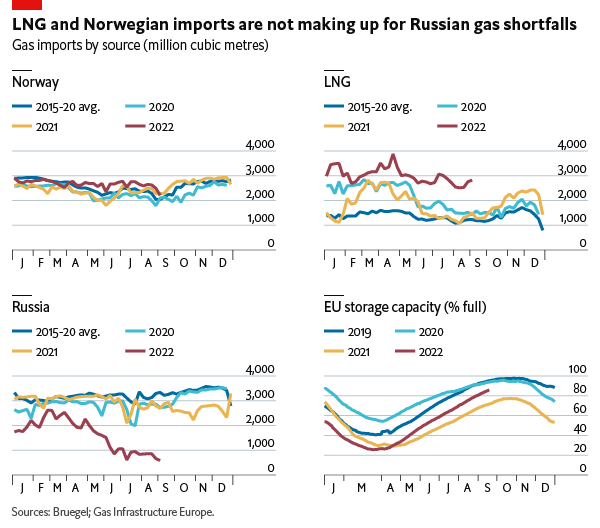
Table of Contents
The Current State of EU Dependence on Russian Gas
For decades, the EU relied heavily on Russia for its natural gas needs. This reliance wasn't simply a matter of convenience; it was deeply ingrained in the energy infrastructure and trade relationships developed over years. Before the conflict in Ukraine, Russia supplied a significant portion of the EU's gas, making it a dominant player in the European energy market and giving it considerable geopolitical leverage.
- Percentage of EU gas imports sourced from Russia (pre-conflict): Approximately 40%, varying significantly between member states.
- Key EU countries most heavily reliant on Russian gas: Germany, Italy, and Austria were among the most dependent.
- Economic consequences of Russian gas supply disruptions: Supply cuts resulted in soaring energy prices, impacting industries and consumers alike, leading to inflation and economic uncertainty.
- Geopolitical vulnerabilities associated with reliance on a single supplier: The dependence on Russia created significant vulnerabilities, leaving the EU susceptible to political pressure and energy blackmail.
The EU's Strategy to Reduce Reliance on Russian Spot Market Gas
The EU's response to the energy crisis has been multifaceted, encompassing a decisive move away from the Russian spot market for natural gas. This strategy involves a combination of measures aimed at diversifying supply sources, boosting domestic production, and accelerating the transition to renewable energy.
- Increased investments in renewable energy sources (solar, wind, etc.): Massive investments are being channeled into renewable energy infrastructure, aiming for a significant increase in the share of renewables in the EU's energy mix.
- Development of strategic gas storage facilities across the EU: The EU is building up its gas storage capacity to ensure sufficient reserves for peak demand and to mitigate the impact of supply disruptions.
- Expansion of LNG import terminals: The construction and expansion of liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals are crucial to importing gas from alternative suppliers.
- Diversification of gas suppliers (Norway, USA, Qatar, etc.): The EU is actively seeking alternative sources of natural gas from countries like Norway, the USA, and Qatar, lessening its dependence on Russia.
- EU sanctions targeting Russian energy companies: Sanctions have been imposed on Russian energy companies to limit their ability to export gas to the EU.
Challenges and Obstacles in the Transition
The shift away from Russian gas isn't without its hurdles. The transition requires substantial investments, logistical adjustments, and political cooperation.
- High costs of transitioning to alternative energy sources: The upfront investment required for renewable energy infrastructure and LNG terminals is substantial.
- Potential energy price increases for consumers: The transition may lead to temporary price increases as the EU adjusts to a new energy mix.
- Infrastructure limitations for importing LNG: The existing infrastructure might not be sufficient to handle the increased volume of LNG imports, requiring upgrades and expansion.
- Political challenges in securing alternative gas supplies: Negotiating long-term gas supply agreements with alternative providers involves complex political and economic considerations.
The Long-Term Vision: Achieving European Energy Independence
The EU's long-term energy strategy aims for a future of energy independence and sustainability. This involves a significant increase in renewable energy, improved energy efficiency, and a reduction in reliance on fossil fuels.
- Target percentage of renewable energy in the EU's energy mix by a specific year: The EU has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, aiming for a significant percentage by 2030 and beyond.
- Investments in energy efficiency measures: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry is a key component of the strategy.
- Plans for developing domestic gas production: Exploring and developing domestic gas resources can contribute to reducing reliance on imports.
- EU’s collaboration with other countries to secure long-term energy partnerships: The EU is strengthening partnerships with reliable energy suppliers to ensure stable and secure energy supplies for the future.
Conclusion
The EU's plan to end its reliance on Russian gas imports represents a monumental undertaking. The crackdown on the spot market is a crucial step in this broader strategy of energy diversification and the pursuit of energy independence. While significant challenges remain, including high transition costs and infrastructural limitations, the EU's commitment to renewable energy and alternative suppliers is paving the way for a more secure and sustainable energy future. Staying informed about the progress of this vital initiative is crucial. Follow our updates for the latest insights into the Spot Market Crackdown and the EU's journey towards energy independence.

Featured Posts
-
 Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment Found In Buildings After Months
Apr 24, 2025
Toxic Chemical Residue From Ohio Train Derailment Found In Buildings After Months
Apr 24, 2025 -
 New Business Hot Spots Where To Invest And Grow In Country Name
Apr 24, 2025
New Business Hot Spots Where To Invest And Grow In Country Name
Apr 24, 2025 -
 India Market Buzz Niftys Bullish Run Fueled By Positive Trends
Apr 24, 2025
India Market Buzz Niftys Bullish Run Fueled By Positive Trends
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Hopes Double Trouble Liams Pledge And Lunas Bold Move The Bold And The Beautiful Preview
Apr 24, 2025
Hopes Double Trouble Liams Pledge And Lunas Bold Move The Bold And The Beautiful Preview
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Anchor Brewing Company To Shutter A Legacy Ends
Apr 24, 2025
Anchor Brewing Company To Shutter A Legacy Ends
Apr 24, 2025
