The Dax: A Reflection Of German Politics And The Economy

Table of Contents
The German Economy and its Impact on the DAX
The DAX's performance is intrinsically linked to the health of the German economy. Its composition, featuring giants of German industry, provides a direct window into the country's economic strengths and vulnerabilities.
Key Economic Sectors Driving the DAX
Several key sectors significantly influence the DAX's trajectory. These include:
-
Automobiles: Companies like Volkswagen, BMW, and Daimler are DAX heavyweights. Their performance, influenced by global demand, technological innovation (electric vehicles, autonomous driving), and supply chain issues, heavily impacts the index. A downturn in the automotive sector can trigger a significant DAX decline.
-
Technology: The German technology sector, though not as dominant as in the US, is increasingly influential. Companies focused on software, industrial automation, and renewable energy contribute to DAX growth. Technological advancements and global competition are key drivers here.
-
Chemicals: Germany boasts a robust chemical industry, with companies like BASF playing a crucial role in the DAX. This sector's performance is cyclical, influenced by global commodity prices and industrial output. Economic downturns often impact the chemical sector disproportionately.
-
Financials: Major German banks and insurance companies contribute to the DAX. Their performance reflects the overall health of the financial system and investor confidence. Interest rate changes by the European Central Bank (ECB) directly impact this sector.
These sectors are influenced by major economic indicators:
- GDP Growth: A strong GDP usually correlates with a rising DAX.
- Inflation: High inflation erodes purchasing power and can negatively affect corporate profits, impacting the DAX.
- Unemployment: Low unemployment generally boosts consumer spending and business confidence, leading to a healthier DAX.
Global Economic Factors Influencing the DAX
The DAX is not immune to global economic forces. External factors significantly impact its performance:
-
Global Trade Wars: Trade disputes can disrupt supply chains and reduce export opportunities for German companies, negatively affecting the DAX.
-
ECB Interest Rate Changes: ECB monetary policy directly affects borrowing costs for German businesses and influences investor sentiment, impacting DAX fluctuations.
-
Performance of Other Major Stock Markets: The DAX's performance is often correlated with other major indices like the Dow Jones and FTSE. A global market downturn will likely affect the DAX negatively.
-
Energy Prices: Fluctuations in energy prices, especially since the war in Ukraine, significantly affect manufacturing costs and overall economic output, creating volatility in the DAX.
-
Supply Chain Disruptions: Global supply chain bottlenecks can hamper production and negatively impact the profitability of DAX-listed companies.
German Politics and its Influence on the DAX
German political decisions and events significantly influence the DAX's trajectory. Investor confidence is heavily tied to political stability and the perceived direction of government policy.
Government Policies and Regulatory Changes
Government policies directly impact business confidence and the DAX:
-
Fiscal Policy: Government spending and taxation policies influence business investment and consumer spending. Expansionary fiscal policies can boost the DAX, while austerity measures may have a negative effect.
-
Monetary Policy (indirect): While the ECB sets monetary policy, the German government's economic actions can influence the ECB's decisions and indirectly affect the DAX.
-
Regulatory Changes: Changes in environmental regulations, labor laws, or corporate governance can impact DAX-listed companies' profitability and investor sentiment. For example, stricter emission standards for automobiles could negatively affect car manufacturers' share prices.
Examples of government interventions and their effects:
- Subsidies for renewable energy companies can positively affect their share prices.
- Tax cuts for businesses can boost investment and positively impact the DAX.
- Increased regulations on a particular industry might lead to a decline in related company share prices.
The Role of Political Risk
Political events create uncertainty and influence investor behavior:
-
Elections: Major elections can cause DAX volatility as investors anticipate potential policy shifts.
-
Coalition Negotiations: Lengthy coalition negotiations can create uncertainty and negatively impact investor sentiment.
-
Policy Debates: Public debates on significant policy changes (e.g., energy transition, tax reform) can introduce volatility into the DAX.
Instances where political events caused DAX fluctuations:
- The formation of a new government after an election often leads to short-term market movements.
- Unexpected political crises can trigger significant DAX declines.
Analyzing the DAX: Tools and Strategies
Understanding the DAX requires a multi-faceted approach using both fundamental and technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis of DAX Components
Fundamental analysis focuses on the intrinsic value of individual DAX companies:
-
Financial Statement Analysis: Examine financial statements (income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements) to assess a company's financial health and profitability.
-
Key Financial Ratios: Use ratios like Price-to-Earnings (P/E), Return on Equity (ROE), and Debt-to-Equity to evaluate a company's performance and valuation.
-
Industry Trends: Understanding industry trends and competitive dynamics is crucial for evaluating a company's future prospects.
-
Company-Specific News: Stay informed about company-specific news and announcements that can impact share prices.
Technical Analysis of the DAX Index
Technical analysis uses charts and indicators to predict future price movements:
-
Moving Averages: Track price trends using moving averages (e.g., 50-day, 200-day).
-
RSI (Relative Strength Index): Identify overbought and oversold conditions.
-
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Identify momentum changes.
-
Chart Patterns: Recognize chart patterns (e.g., head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms) to anticipate price reversals.
It's crucial to remember that technical analysis is not foolproof and should be used in conjunction with fundamental analysis.
Conclusion: Understanding the DAX for Informed Investment Decisions
The DAX is a complex index reflecting the interplay of the German economy and its political landscape. Understanding the relationships between these factors is crucial for investors to make informed decisions. Factors ranging from automotive production to ECB interest rates, and from government policy to global trade winds, all play a significant role in shaping the DAX's trajectory. By utilizing a combination of fundamental and technical analysis, along with a keen awareness of the political and economic climate in Germany and globally, investors can better navigate the complexities of the DAX and make more informed investment choices. To deepen your understanding of the DAX, explore resources on German economics, political analysis, and financial market trends. Continue your research and develop a comprehensive understanding of the DAX to navigate this dynamic market effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Werner Herzogs Bucking Fastard A Look At The Sisterly Leads
Apr 27, 2025
Werner Herzogs Bucking Fastard A Look At The Sisterly Leads
Apr 27, 2025 -
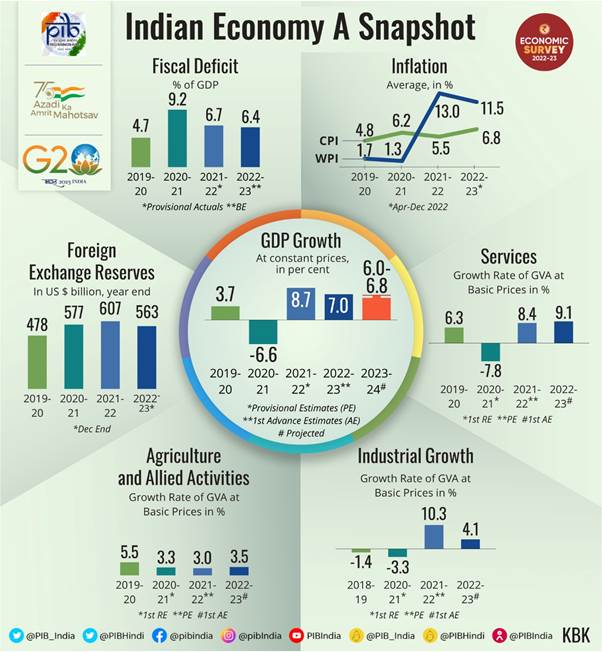 Canadian Travel Boycott A Fed Snapshot Of Economic Impact
Apr 27, 2025
Canadian Travel Boycott A Fed Snapshot Of Economic Impact
Apr 27, 2025 -
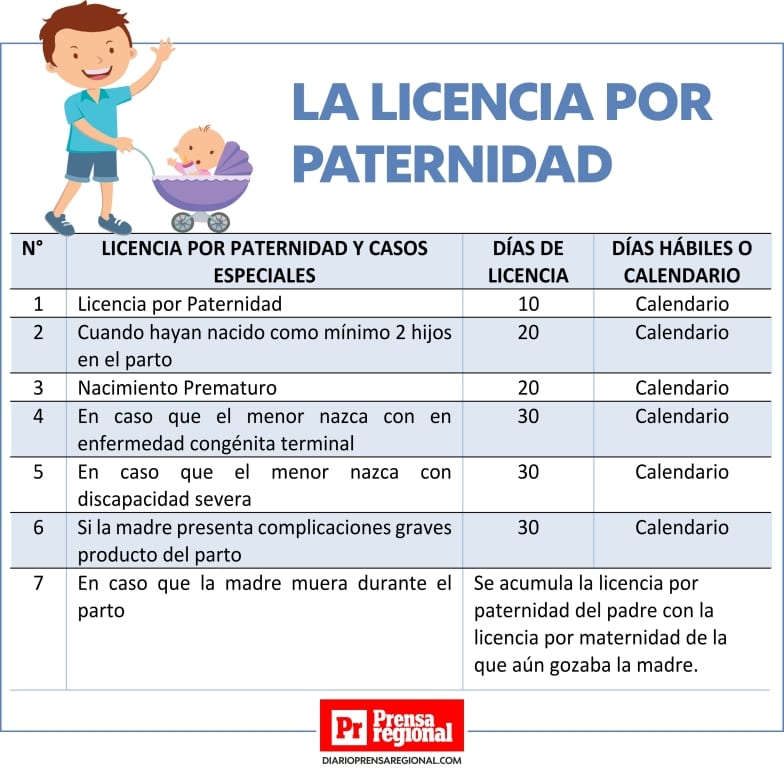 Wta Lidera Un Ano De Pago Por Licencia De Maternidad Para Jugadoras
Apr 27, 2025
Wta Lidera Un Ano De Pago Por Licencia De Maternidad Para Jugadoras
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Juliette Binoche Appointed President Of The Cannes Jury For 2025
Apr 27, 2025
Juliette Binoche Appointed President Of The Cannes Jury For 2025
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Trump Forecasts Imminent Trade Deals Within A Month
Apr 27, 2025
Trump Forecasts Imminent Trade Deals Within A Month
Apr 27, 2025
