How Is A New Pope Chosen? A Complete Guide To Papal Conclaves
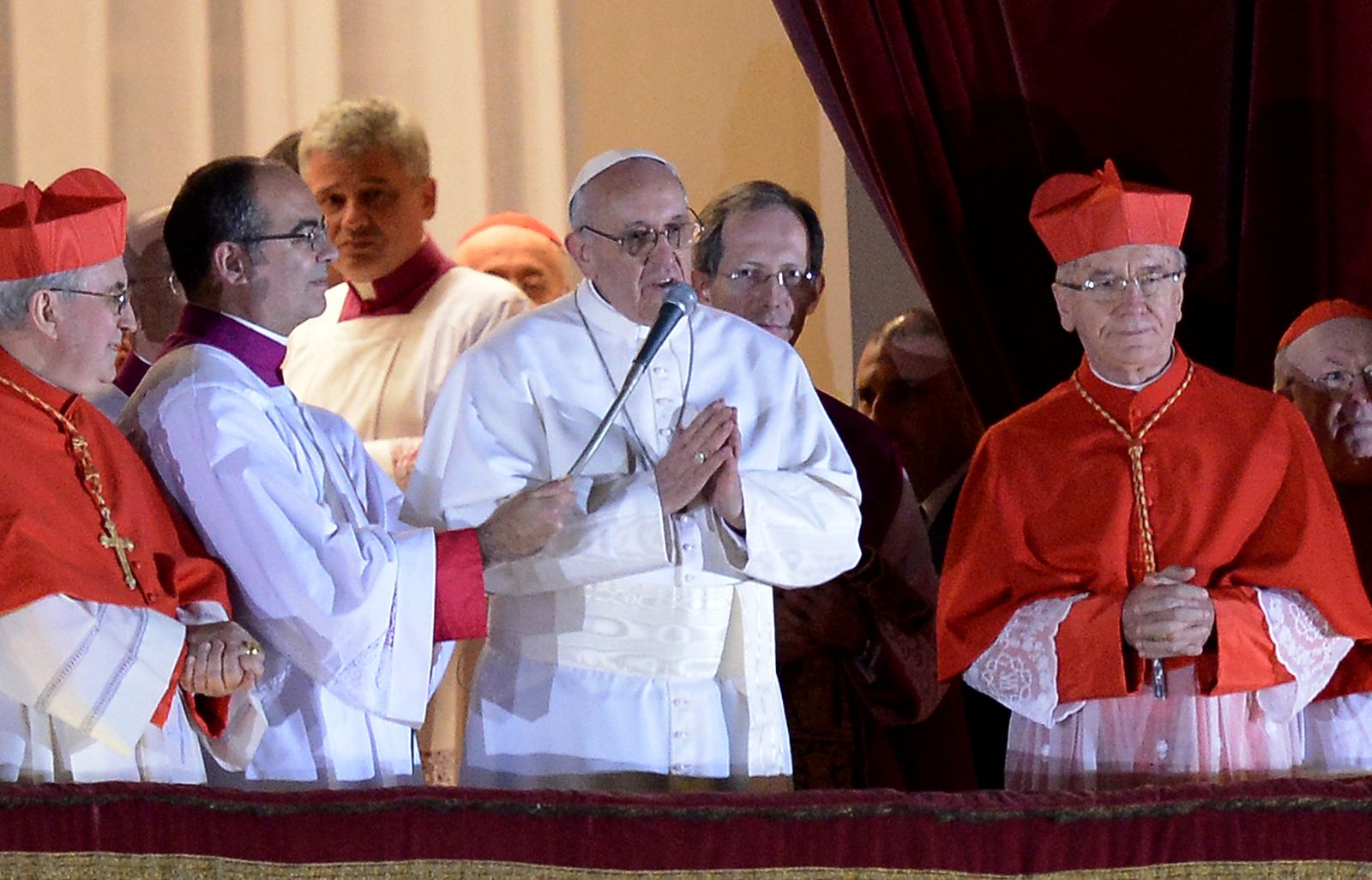

Table of Contents
The Death or Resignation of a Pope
The process of selecting a new Pope begins with the official declaration of a vacancy in the papacy. This occurs upon the death or resignation of the reigning Pope. The death of a Pope, while a solemn occasion, triggers a precise set of procedures. Similarly, a papal resignation, a relatively recent development, follows a carefully defined protocol.
- Confirmation of the Pope's death (or resignation): The death of a Pope is officially confirmed by the Cardinal Camerlengo, a significant figure in the sede vacante period. Resignations are communicated directly and officially by the Pope himself.
- The sede vacante period begins: This period, literally meaning "the vacant see," marks the interim between the death or resignation and the election of the new Pope. During this time, the governance of the Church is temporarily entrusted to specific cardinals.
- The role of the Cardinal Camerlengo during the sede vacante: The Cardinal Camerlengo acts as a kind of temporary administrator, ensuring the smooth running of the Vatican and overseeing preparations for the Papal Conclave. His responsibilities are numerous and critical during this transition period.
The Role of Cardinals in Papal Conclaves
The College of Cardinals, a body of senior clergy appointed by the Pope, plays a central role in Papal Conclaves. Only a select group within this body, known as Cardinal electors, are eligible to participate in the election.
- Cardinal electors: Eligibility criteria (age, etc.): To be eligible, cardinals must be under the age of 80 at the time the vacancy occurs. This ensures a balance of experience and youthful perspectives within the conclave.
- The number of Cardinal electors: The number of cardinal electors varies depending on the number of cardinals who meet the age criterion. This number influences the dynamics and potential outcomes of the conclave.
- The different roles within the College of Cardinals: Beyond the cardinal electors, other cardinals play important roles in the preparatory phases and the conduct of the conclave itself. Their experience and expertise contribute significantly to a smooth and efficient process.
The Conclave: Location, Rules, and Procedures
The Papal Conclave, the actual election process, takes place in a secure location, traditionally the Sistine Chapel within the Vatican Palace. Stringent security measures are implemented to ensure the secrecy and integrity of the process.
- The Sistine Chapel: Its history and significance: The Sistine Chapel, renowned for its artistic masterpieces, holds immense historical and symbolic significance as the venue for Papal Conclaves. Its historical weight lends an air of solemnity to the proceedings.
- Secrecy and communication restrictions: The conclave is characterized by strict rules of secrecy, aimed at minimizing external influences on the cardinals' decisions. Communication with the outside world is strictly limited.
- The voting process: ballots, two-thirds majority required: Cardinals cast secret ballots, and a two-thirds majority is required to elect a new Pope. This threshold ensures a consensus and strengthens the legitimacy of the new pontiff.
The Election Process: From Ballots to White Smoke
The voting process within the conclave is rigorous and carefully regulated. Multiple rounds of voting may be necessary before a two-thirds majority is achieved.
- Preparation and verification of ballots: The preparation and handling of ballots are closely monitored to ensure fairness and transparency.
- Counting the votes: The votes are meticulously counted by appointed officials, and the results are announced immediately following each round of voting.
- Announcing the results: black smoke vs. white smoke: The world watches for the telltale signs: black smoke signifies no election, while white smoke announces the selection of a new Pope. This simple visual signal connects the secluded conclave to the global Catholic community.
After the Election: The New Pope's Inauguration
Once a new Pope is elected, a series of events mark his ascension to the papacy. These events formally introduce the new pontiff to the world.
- The formal announcement from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica: The traditional announcement from the balcony of St. Peter's Basilica signals the election to the global audience.
- The papal coronation (or simple inauguration): Depending on the tradition followed by the new Pope, a formal coronation or a simpler inauguration ceremony may take place.
- The new Pope's first address (Urbi et Orbi): The new Pope's first address, known as Urbi et Orbi ("to the city and to the world"), sets the tone for his papacy and addresses the global community.
Conclusion
Understanding the process of electing a new Pope through Papal Conclaves reveals a rich tapestry of history, tradition, and faith. The process, from the declaration of the sede vacante to the announcement of the new Pope, is a carefully orchestrated blend of ritual and democratic procedure. From the pivotal role of the Cardinals to the symbolic significance of white smoke, each step contributes to the selection of the new leader of the Catholic Church. Delve deeper into this fascinating subject by exploring our other articles on [link to related article] or researching the history of specific Papal Conclaves.

Featured Posts
-
 Office365 Hackers Multi Million Dollar Scheme Exposed
Apr 22, 2025
Office365 Hackers Multi Million Dollar Scheme Exposed
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Chainalysis And Alterya A Merger Of Blockchain And Artificial Intelligence
Apr 22, 2025
Chainalysis And Alterya A Merger Of Blockchain And Artificial Intelligence
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Over The Counter Birth Control A Post Roe Game Changer
Apr 22, 2025
Over The Counter Birth Control A Post Roe Game Changer
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Increased Tension Trump Administration To Slash Another 1 Billion From Harvards Funding
Apr 22, 2025
Increased Tension Trump Administration To Slash Another 1 Billion From Harvards Funding
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Enhanced Security Partnership China And Indonesia Forge Closer Links
Apr 22, 2025
Enhanced Security Partnership China And Indonesia Forge Closer Links
Apr 22, 2025
