Why Is The Canadian Dollar Falling Against Major Currencies?
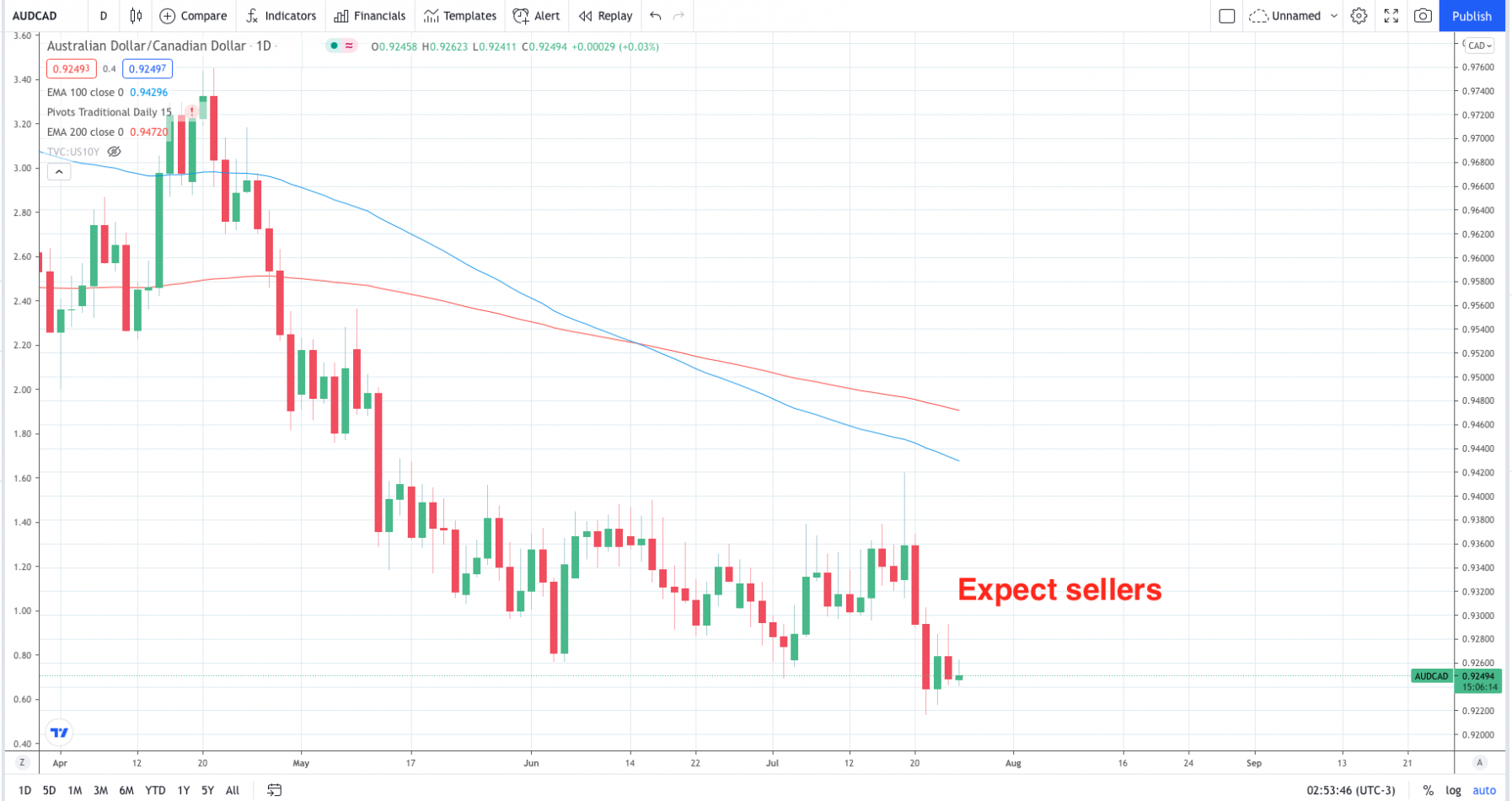
Table of Contents
2.1. Commodity Prices and their Impact on the CAD
The Canadian economy is heavily reliant on the export of raw commodities. Oil, natural gas, and lumber are particularly significant contributors to the nation's GDP. The global demand for and price of these commodities directly influences the value of the Canadian dollar. A decline in commodity prices weakens the CAD because it reduces the demand for the currency from international buyers. This is a fundamental relationship between the Canadian economy and its currency.
- Global oil demand and supply dynamics: OPEC production cuts, global economic growth, and geopolitical instability all affect oil prices and consequently the CAD.
- Impact of geopolitical events on energy prices: Conflicts in oil-producing regions can disrupt supply and send prices soaring, temporarily boosting the CAD. Conversely, periods of relative peace can lead to lower prices.
- Fluctuations in lumber prices due to global construction activity: The global housing market and construction activity directly influence lumber demand and therefore Canadian lumber exports. Strong demand strengthens the CAD, while weak demand weakens it.
- The relationship between commodity prices and the Canadian dollar exchange rate: This is a strong correlation; when commodity prices rise, the CAD tends to strengthen, and vice versa. This makes the CAD a "commodity currency," highly sensitive to global commodity market trends.
Example: A global recession reducing demand for oil would depress oil prices, lessening international demand for Canadian dollars and leading to a weaker CAD against other major currencies.
2.2. Interest Rate Differentials and Monetary Policy
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining currency exchange rates. The Bank of Canada's monetary policy, specifically its decisions on interest rate adjustments, significantly impacts the CAD's value. When Canadian interest rates are lower compared to other major economies, investors may seek higher returns elsewhere, reducing demand for the CAD and weakening it.
- The Bank of Canada's monetary policy decisions and their effect on interest rates: The Bank of Canada's mandate is to maintain price stability and full employment. Interest rate adjustments are a key tool used to achieve these goals. Higher interest rates typically attract foreign investment, strengthening the CAD.
- Comparison of Canadian interest rates with those of major economies (e.g., US, EU, UK): The difference between Canadian interest rates and those in other countries significantly influences capital flows. A higher differential attracts investment, increasing demand for CAD.
- Investor behavior and capital flows based on interest rate differentials: Investors seek the highest returns for their investments. When interest rates in another country are higher, funds flow to that country, potentially weakening the CAD.
Example: If the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates significantly while the Bank of Canada maintains its current rate, investors might shift funds to the US, driving up the USD and weakening the CAD.
2.3. Geopolitical Factors and Economic Uncertainty
Global events significantly impact investor sentiment and, therefore, currency values. Geopolitical instability, economic uncertainty, and political risk can all contribute to a weakening Canadian dollar. Investor confidence is a key driver of currency values.
- Impact of global trade wars and protectionist policies: Trade disputes can disrupt supply chains and reduce global trade, negatively affecting commodity prices and the CAD.
- Influence of political instability in Canada or major trading partners: Political uncertainty in Canada or its major trading partners can lead to capital flight and a weaker CAD.
- Investor sentiment and risk aversion in response to global events: During periods of global uncertainty, investors often favor "safe-haven" currencies like the USD, leading to a weaker CAD.
- The effect of global economic slowdowns on the Canadian dollar: Global recessions typically reduce demand for commodities and weaken the CAD.
Example: A major trade war impacting Canadian exports would likely result in reduced demand for the CAD, causing its value to fall.
2.4. US Dollar Strength and its Correlation with the CAD
The US dollar's strength is intrinsically linked to the CAD's value. As the world's reserve currency, the USD's performance significantly impacts other currencies, including the CAD. A strengthening USD often leads to a weaker CAD.
- The relationship between the USD and other major currencies: The USD's value relative to other major currencies significantly impacts the CAD. A stronger USD usually implies a weaker CAD.
- How US economic performance influences the USD and indirectly affects the CAD: Strong US economic growth typically strengthens the USD, indirectly weakening the CAD.
- The impact of US monetary policy on the USD and the CAD: US Federal Reserve decisions on interest rates directly influence the USD's value and indirectly impact the CAD.
Example: Increased investor confidence in the US economy, leading to a stronger USD, will likely put downward pressure on the Canadian dollar.
3. Conclusion
The Canadian dollar's exchange rate is a complex reflection of global economic forces, including commodity prices, interest rate differentials, geopolitical events, and the strength of the US dollar. Understanding these interconnected factors is vital for businesses, investors, and individuals managing their finances in a globalized world. To make informed decisions about investments and international transactions involving the Canadian dollar, continue to monitor global economic news, analyze commodity markets, and consult with financial experts. Stay informed on why the Canadian dollar is falling or rising to effectively manage your financial exposure.

Featured Posts
-
 Canadian Dollar Performance Mixed Signals Amidst Global Market Volatility
Apr 24, 2025
Canadian Dollar Performance Mixed Signals Amidst Global Market Volatility
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Watch John Travoltas Pulp Fiction Inspired Steak Dinner In Miami
Apr 24, 2025
Watch John Travoltas Pulp Fiction Inspired Steak Dinner In Miami
Apr 24, 2025 -
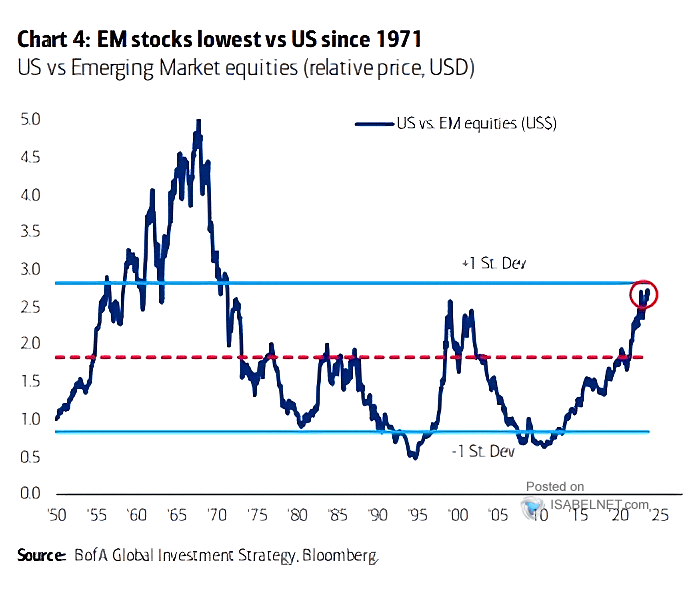 Strong Performance Of Emerging Market Stocks In Contrast To Us Decline
Apr 24, 2025
Strong Performance Of Emerging Market Stocks In Contrast To Us Decline
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Drop In Illegal Border Crossings Between U S And Canada White House Data
Apr 24, 2025
Drop In Illegal Border Crossings Between U S And Canada White House Data
Apr 24, 2025 -
 The Fishermans Ring The Ritual Destruction Following A Popes Passing
Apr 24, 2025
The Fishermans Ring The Ritual Destruction Following A Popes Passing
Apr 24, 2025
