Assessing The Impact Of Trump's Trade Offensive On US Economic Power

Table of Contents
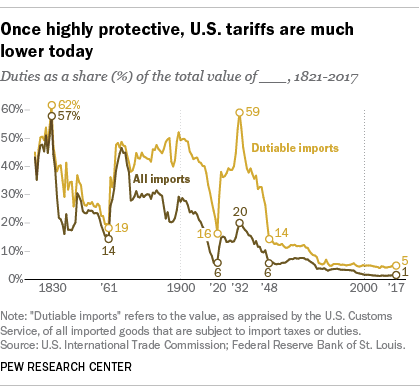
The Tariffs and Their Immediate Effects
Impact on Specific Industries
Trump's tariffs, particularly those targeting China, had a significant impact on various US industries. The term "trade war effects" became a common phrase as retaliatory tariffs from other countries exacerbated the situation. A sectoral analysis reveals a mixed bag:
- Agriculture: The agricultural sector suffered significantly due to retaliatory tariffs imposed by China, impacting exports of soybeans, pork, and other agricultural products. Employment in some agricultural sectors declined, and farm incomes were negatively affected. [Source: USDA Economic Research Service reports]
- Manufacturing (Steel & Aluminum): While domestic steel and aluminum producers initially benefited from increased protection, the higher prices for these inputs negatively impacted downstream industries, leading to increased costs and reduced competitiveness for manufacturers of goods using steel and aluminum. [Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis data]
- Technology: The technology sector was impacted by tariffs on various components and goods, impacting both production costs and supply chains. The resulting uncertainty led to decreased investment in some areas. [Source: Semiconductor Industry Association reports]
The imposition of these tariffs, and the resulting "tariff impact," led to significant trade friction and uncertainty.
Consumer Price Changes
The tariffs led to increased inflationary pressures, impacting the consumer price index (CPI). The "tariff burden" was not evenly distributed. While some industries saw price increases, others were impacted indirectly through supply chain disruptions.
- Specific products subject to tariffs, such as washing machines and steel products, experienced noticeable price hikes. [Source: Consumer Price Index data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics]
- The increased cost of inputs due to tariffs resulted in higher prices for a range of consumer goods, impacting low- and middle-income households disproportionately.
Shifting Global Trade Relationships
Renegotiation of Trade Agreements
The renegotiation of NAFTA into the USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) represents a significant shift in US trade policy. The "trade agreement renegotiation" process aimed to address perceived imbalances and improve conditions for US businesses.
- While the USMCA aimed to modernize trade rules, the overall impact on trade volumes with Canada and Mexico remains a subject of ongoing debate, with some sectors benefiting and others experiencing losses. [Source: USMCA data from the Office of the United States Trade Representative]
- The renegotiation process and its outcome significantly impacted bilateral trade agreements and the overall relationship between the US and its closest trading partners.
Rise of Protectionism and its Consequences
Trump's protectionist stance significantly impacted global trade relations. The challenges posed to the WTO (World Trade Organization) and the escalating trade disputes highlighted the risks of unilateral trade actions.
- Retaliatory tariffs from other countries disrupted global supply chains, causing delays and increased costs for businesses worldwide.
- The rise of protectionism fueled uncertainty, impacting business investment and slowing down global economic growth. [Source: World Bank and IMF reports]
Long-Term Economic Consequences
Investment and Productivity
The trade uncertainty created by Trump's policies negatively affected business investment and productivity growth. The uncertainty surrounding future trade relations discouraged long-term planning and investment.
- Data suggests a decrease in business investment in sectors heavily impacted by tariffs and trade disputes. [Source: Federal Reserve data on business investment]
- The resulting reduced investment and increased uncertainty potentially hindered innovation and long-term productivity growth, impacting US competitiveness in the global market.
National Debt and Deficit
Trump's trade policies had a complex impact on the US national debt and deficit. While some argue that tariffs increased government revenue, others point to the negative effects on economic growth, ultimately increasing the deficit.
- The trade wars and their impact on various sectors affected government revenue through changes in tax collections and increased spending on trade-related programs. [Source: Congressional Budget Office reports]
- The overall effect on the national debt and deficit is still being debated, with economists offering different assessments depending on the models and assumptions used.
Conclusion
Trump's trade offensive had a multifaceted impact on the US economy. While some sectors experienced short-term gains from protectionist measures, the overall effect appears to have been negative, contributing to increased economic uncertainty, inflationary pressures, and potentially hindering long-term productivity growth. The long-term implications for US economic power and global trade relations remain a subject of ongoing debate and further research. Understanding the long-term consequences of Trump's trade offensive requires continued analysis. Further research into the effects on specific sectors such as agriculture and technology and the broader implications for US economic power is crucial.

Featured Posts
-
 Navigating The Chinese Market The Struggles Of Bmw Porsche And Competitors
Apr 22, 2025
Navigating The Chinese Market The Struggles Of Bmw Porsche And Competitors
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Hegseth Family And Classified Information Signal Chat Investigation
Apr 22, 2025
Hegseth Family And Classified Information Signal Chat Investigation
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Chinas Economy Exposed By Reliance On Exports And Tariffs
Apr 22, 2025
Chinas Economy Exposed By Reliance On Exports And Tariffs
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Stock Investors Push Market Higher Despite Looming Losses
Apr 22, 2025
Stock Investors Push Market Higher Despite Looming Losses
Apr 22, 2025 -
 The Countrys New Business Landscape A Regional Overview
Apr 22, 2025
The Countrys New Business Landscape A Regional Overview
Apr 22, 2025
