China's Economy: Exposed By Reliance On Exports And Tariffs
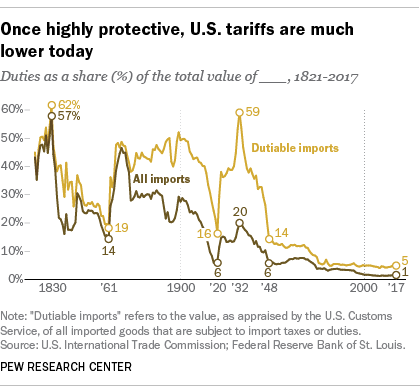
Table of Contents
The Export-Oriented Engine of China's Economic Growth
China's remarkable economic ascent is inextricably linked to its prowess as a global manufacturing powerhouse. This export-oriented strategy has propelled its GDP to remarkable heights, making it a dominant player in international trade.
Manufacturing Powerhouse and Global Supply Chains
China's dominance in global manufacturing is undeniable. Its integration into international supply chains is so extensive that it's become the cornerstone of many global businesses' production processes. Key export sectors, including electronics, textiles, machinery, and consumer goods, contribute significantly to China's GDP.
- China's share of global manufacturing output: Estimates place China's share at over 28%, dwarfing other nations.
- Top export destinations and their import reliance on China: The United States, the European Union, and ASEAN countries are heavily reliant on Chinese goods, showcasing the scale of China's export reach.
- Examples of flagship Chinese export products: From smartphones and computers to clothing and industrial equipment, the diversity and volume of Chinese exports are staggering.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has played a crucial role in supporting these export industries. Multinational corporations have established extensive manufacturing operations in China, leveraging its low labor costs and efficient infrastructure.
The "World's Factory" Model and its Limitations
While the "World's Factory" model has fueled China's growth, its limitations are becoming increasingly apparent. Over-reliance on low-cost manufacturing and exports creates vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability to global economic downturns and shifts in demand: A global recession or a sudden shift in consumer preferences can significantly impact China's export-dependent economy.
- Dependence on specific trading partners and geopolitical risks: The US-China trade war highlighted the risks associated with dependence on specific trading partners and escalating geopolitical tensions.
- The need for economic diversification and upgrading: China needs to shift towards higher value-added manufacturing and reduce its reliance on low-margin export products. This requires substantial investment in research and development, technological innovation, and human capital. Environmental concerns and labor practices associated with rapid export-led growth also demand urgent attention.
The Impact of Tariffs and Trade Wars on China's Economy
The imposition of tariffs, particularly during the US-China trade war, significantly impacted China's economy.
The US-China Trade War and its Consequences
The US-China trade war, characterized by reciprocal tariff increases, disrupted global trade flows and caused economic uncertainty.
- Specific examples of tariffs imposed and their impact on specific sectors: Tariffs on Chinese steel, aluminum, and consumer electronics led to price increases and reduced market share for Chinese businesses.
- Economic data illustrating the effects on GDP growth and trade balances: While the overall impact was complex, studies suggest that the trade war negatively affected both China's GDP growth and its trade balance.
- Analysis of the winners and losers in the trade war: Some sectors, particularly those focused on domestic consumption, experienced benefits, while export-oriented industries suffered.
Navigating Global Trade Tensions and Geopolitical Risks
In response to trade tensions, China is actively seeking to diversify its export markets and reduce its dependence on the US.
- Examples of new trade agreements and partnerships: China's involvement in the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) are key initiatives aimed at expanding trade relationships.
- Challenges in accessing new markets and overcoming trade barriers: Gaining access to new markets requires navigating complex regulations, competing with established players, and overcoming various trade barriers.
- Risks associated with increasing reliance on other specific regions: Over-dependence on any single region exposes China to similar risks as its previous reliance on the US.
Conclusion
China's economic success story is undeniably linked to its export-oriented strategy. However, the increasing reliance on exports and the impact of trade tariffs expose significant vulnerabilities. While China has shown resilience and adaptability, the long-term sustainability of this model remains a key concern. Diversification, technological advancement, and a move towards a more domestically driven economy are crucial for mitigating risks associated with reliance on exports and tariffs. Understanding the intricacies of China's economy and its dependence on global trade is paramount for businesses and policymakers alike. Further research and analysis of China's economy, specifically its reliance on exports and tariffs, are vital for navigating the complexities of the global economic landscape. To stay informed about the evolving dynamics of China's economy and its relationship with global trade, continue researching the impact of China's reliance on exports and tariffs.

Featured Posts
-
 Stock Market Pain Investors Brace For Further Losses
Apr 22, 2025
Stock Market Pain Investors Brace For Further Losses
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Live Stock Market Updates Dow Futures Dollar And Trade War Concerns
Apr 22, 2025
Live Stock Market Updates Dow Futures Dollar And Trade War Concerns
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Trumps Economic Agenda Winners And Losers
Apr 22, 2025
Trumps Economic Agenda Winners And Losers
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Exclusive Report Harvard Loses 1 Billion In Trump Administration Funding Cuts
Apr 22, 2025
Exclusive Report Harvard Loses 1 Billion In Trump Administration Funding Cuts
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Major Canadian Bread Price Fixing Settlement Nears May Hearing Scheduled
Apr 22, 2025
Major Canadian Bread Price Fixing Settlement Nears May Hearing Scheduled
Apr 22, 2025
